Being self-employed comes with many benefits, including the freedom to work on your terms and be your boss. However, it also brings with it the responsibility of managing your finances and staying on top of your tax obligations. To make this process easier, a self-employment ledger can be an invaluable tool.
In this article, we will explore what a self-employment ledger is, why it is important, how to create one, and provide some examples and tips for successful financial management.
What is a Self-Employment Ledger?
A self-employment ledger is a document used by self-employed individuals to keep track of their income, expenses, and other financial transactions. It serves as a record-keeping tool and helps in accurately reporting income and claiming deductions when filing taxes. The ledger typically includes columns for date, description of the transaction, income or expense category, and the amount.
The ledger can be created using a spreadsheet software like Microsoft Excel or Google Sheets, or it can be printed out and filled in manually. Having a version allows for more flexibility and convenience, especially for those who prefer a pen-and-paper approach or want to keep physical copies for their records.
Why is a Self-Employment Ledger Important?
Keeping a self-employment ledger is essential for several reasons:
- Accurate Financial Records: The ledger helps you maintain accurate and up-to-date records of your income and expenses. This is important for monitoring your business’s financial health, tracking your cash flow, and making informed financial decisions.
- Tax Compliance: By keeping a detailed ledger, you can easily report your income and claim deductions when filing your taxes. This reduces the risk of errors, omissions, or audits from the tax authorities.
- Optimizing Tax Refunds: A well-maintained ledger allows you to identify deductible expenses and maximize your tax deductions, potentially leading to a higher tax refund.
- Business Analysis: The ledger provides valuable insights into your business’s performance, allowing you to identify trends, areas of improvement, and make informed decisions for growth.
How to Create a Self-Employment Ledger
Creating a self-employment ledger is a straightforward process. Here are the steps to follow:
1. Determine the Ledger Format
Decide whether you want to create your ledger electronically using spreadsheet software or prefer a version. Choose a format that suits your preferences and needs.
2. Set Up the Columns
Create columns for the date, transaction description, income or expense category, and amount. You may also include additional columns for notes or reference numbers, depending on your requirements.
3. Categorize Your Transactions
Establish a set of income and expense categories that align with your business. Common categories include sales, services, supplies, advertising, utilities, and travel expenses. Consistently categorize each transaction to maintain organization and ease of reference.
4. Record Transactions Regularly
Make it a habit to record your transactions regularly. Set aside dedicated time each week or month to update your ledger. This ensures that your records are accurate and up-to-date.
5. Review and Reconcile
Regularly review your ledger to identify any errors, discrepancies, or missing entries. Reconcile your ledger with bank statements and other financial records to ensure accuracy.
6. Back Up Your Ledger
Take regular backups of your electronic ledger or make copies of your ledger. Store the backups securely to protect against data loss or damage.
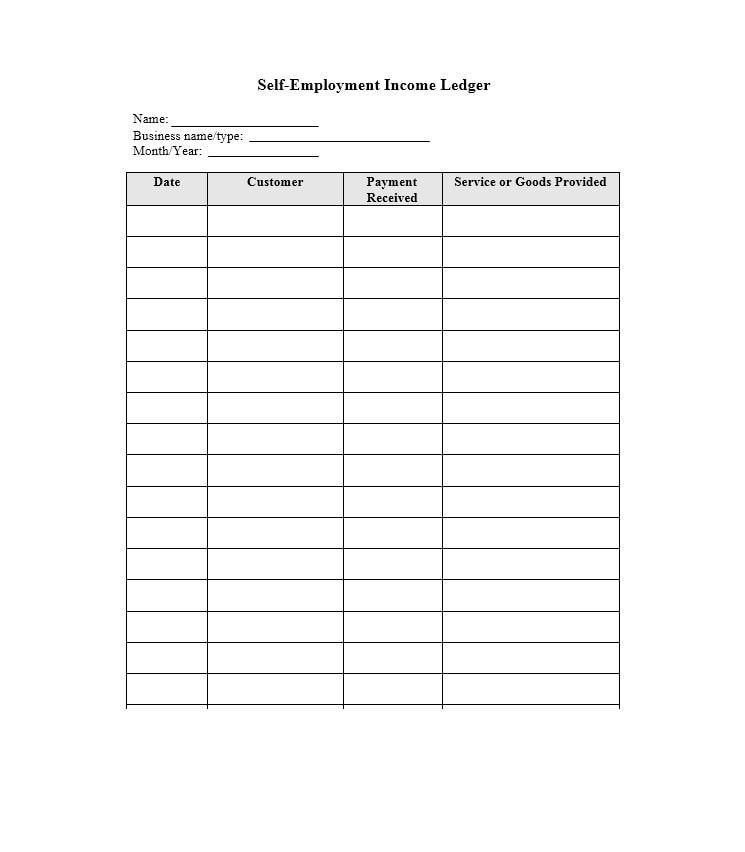
Examples of Self-Employment Ledgers
Here are a few examples of how a self-employment ledger may look:
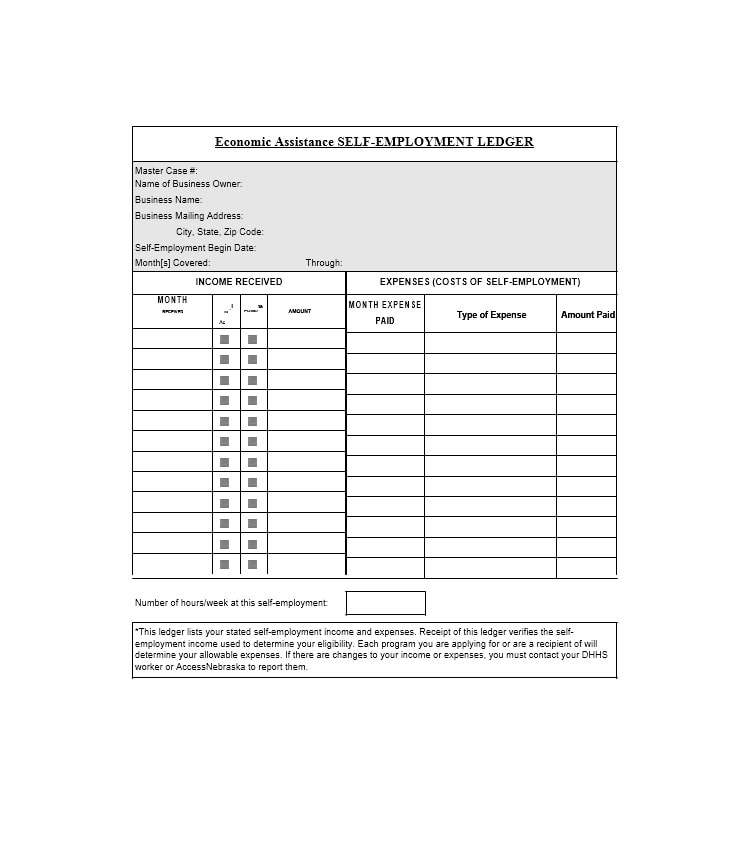
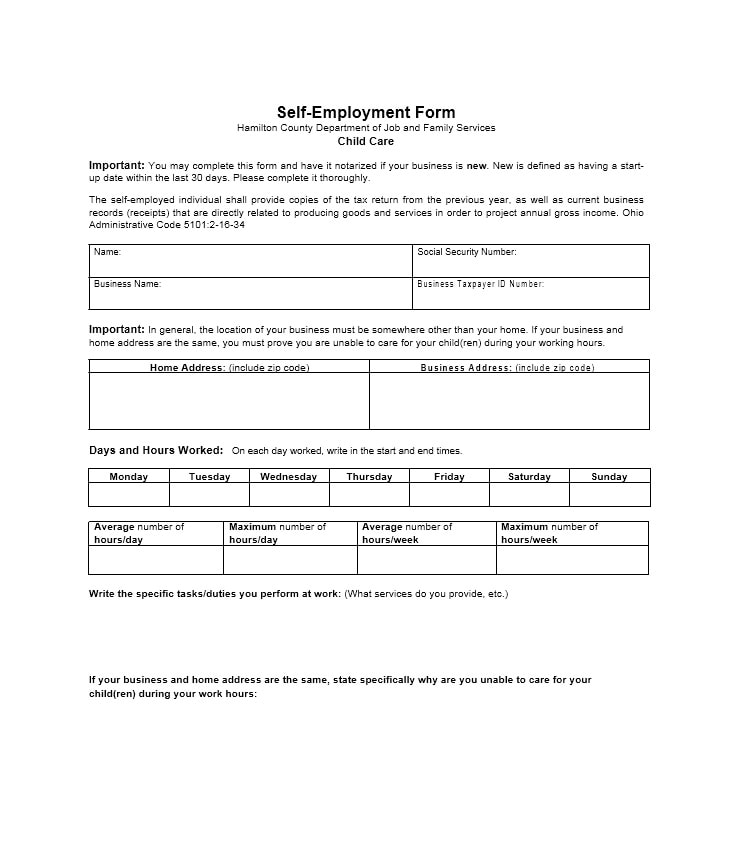
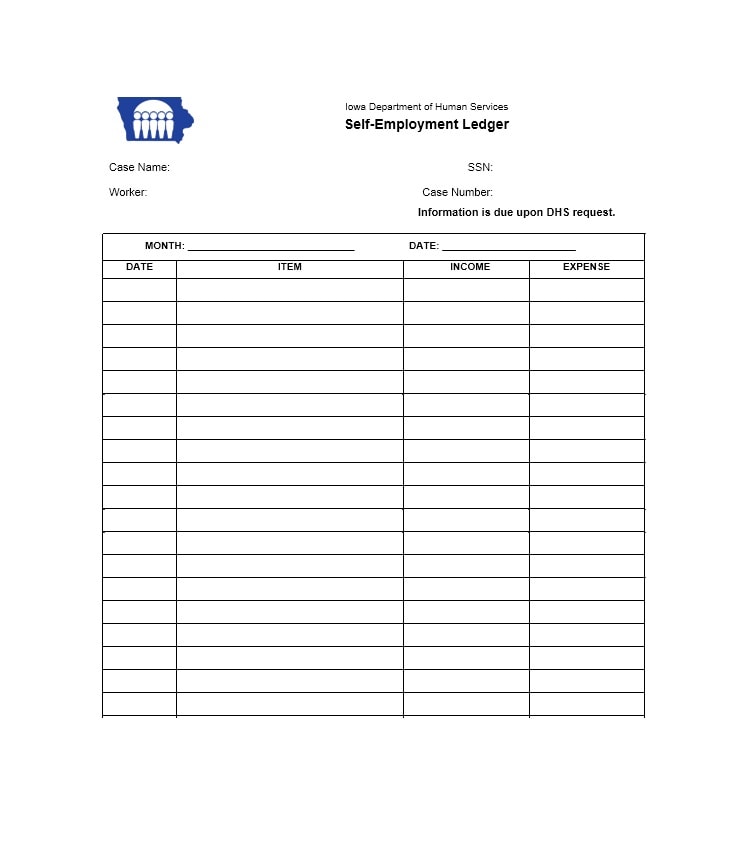





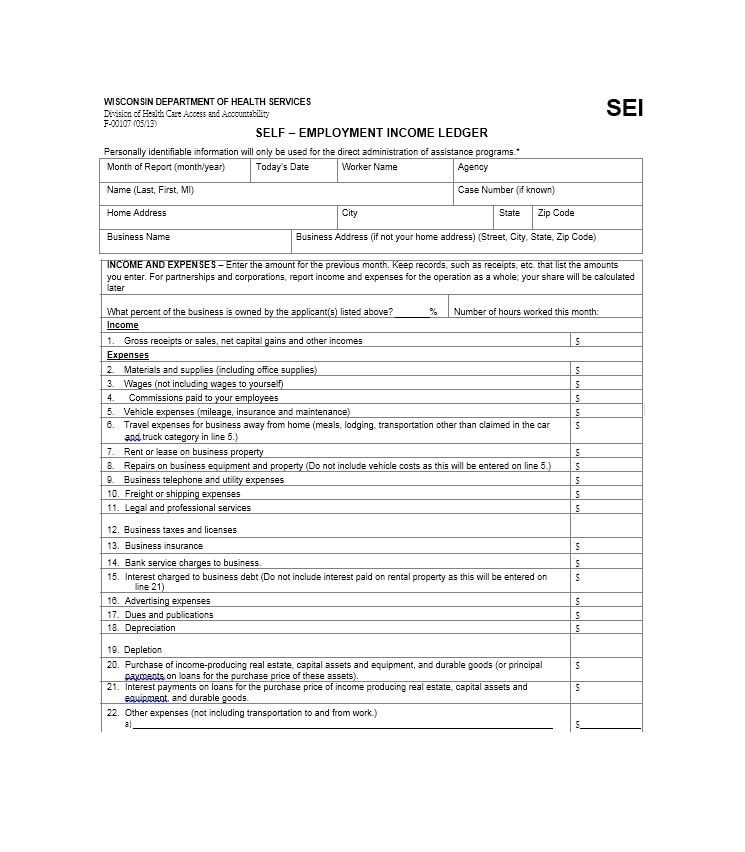
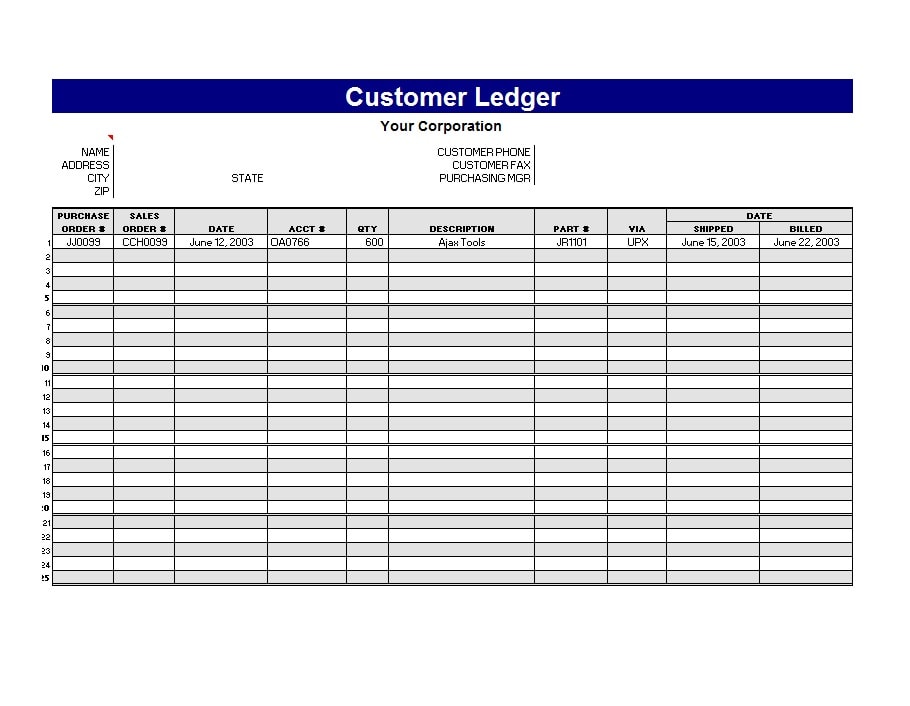
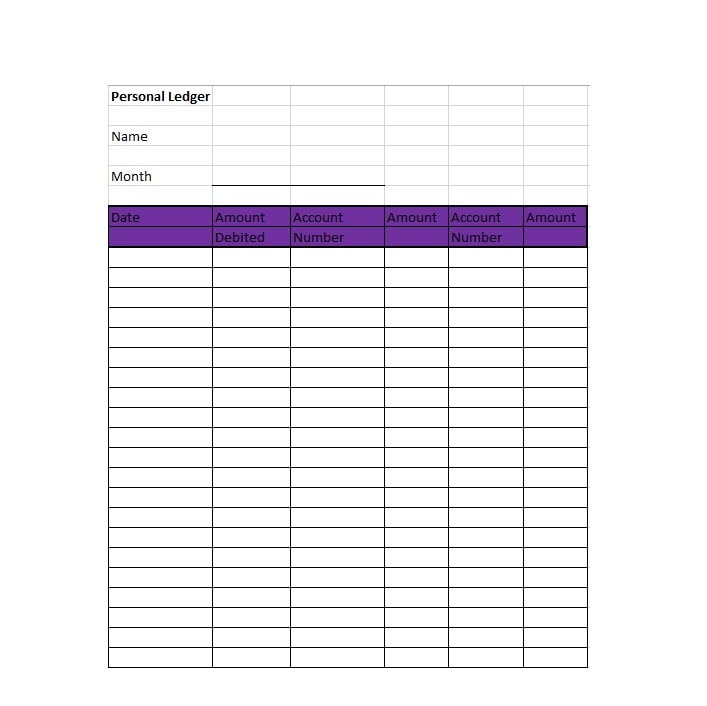
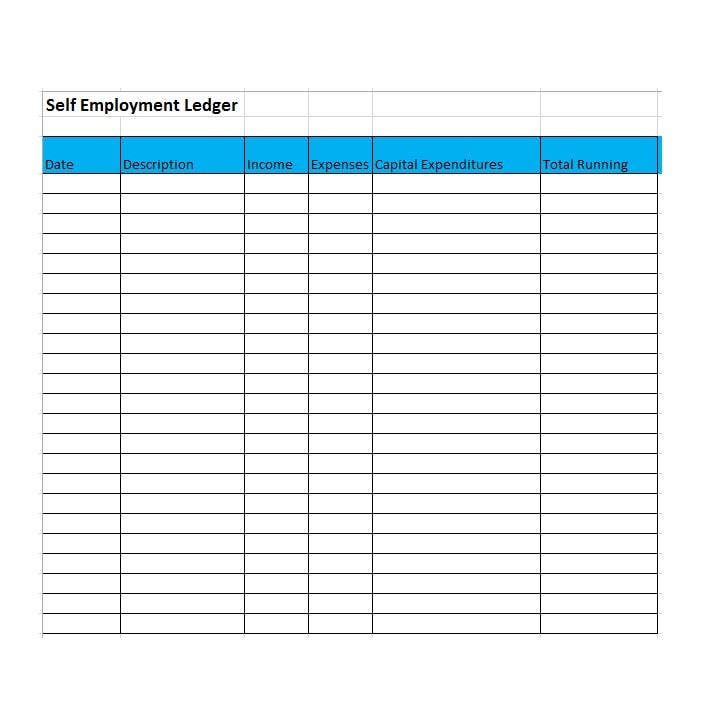
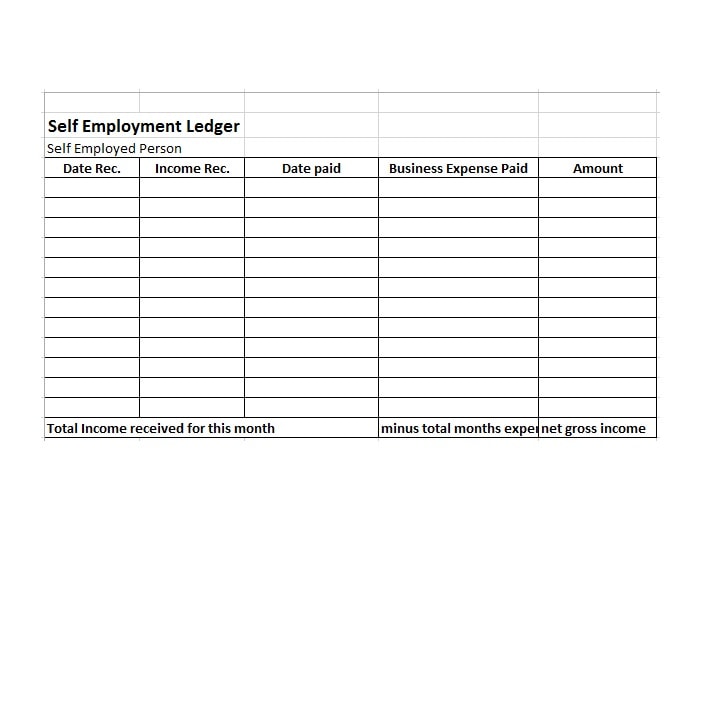
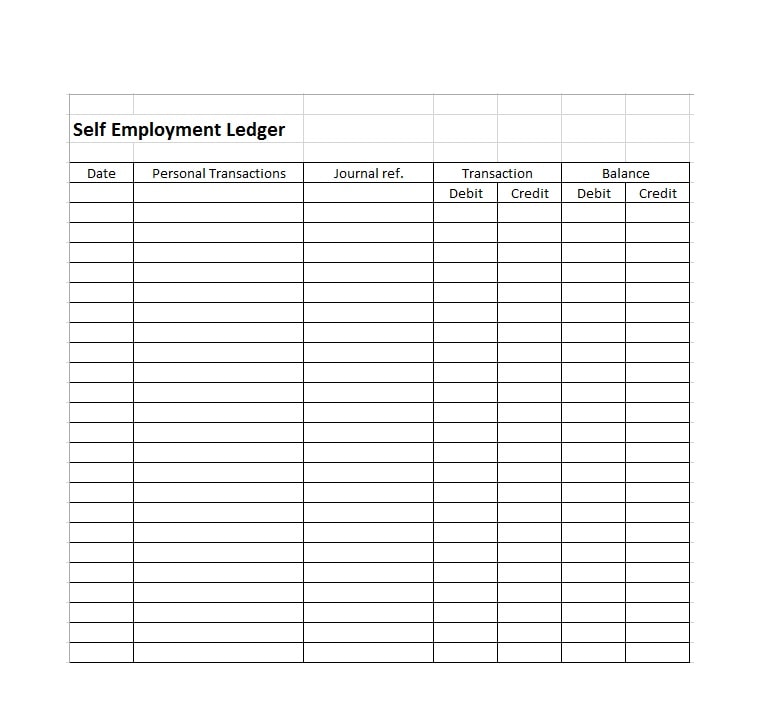
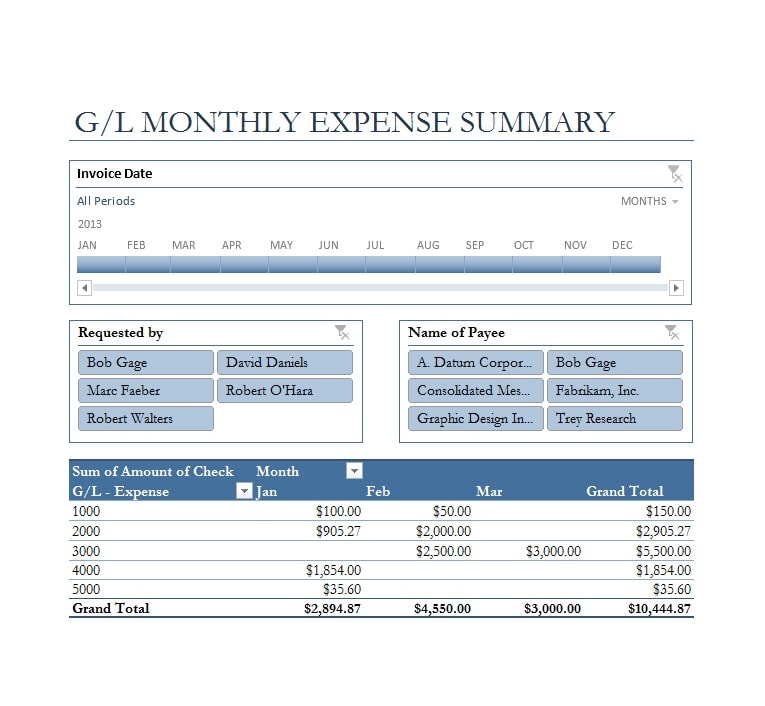
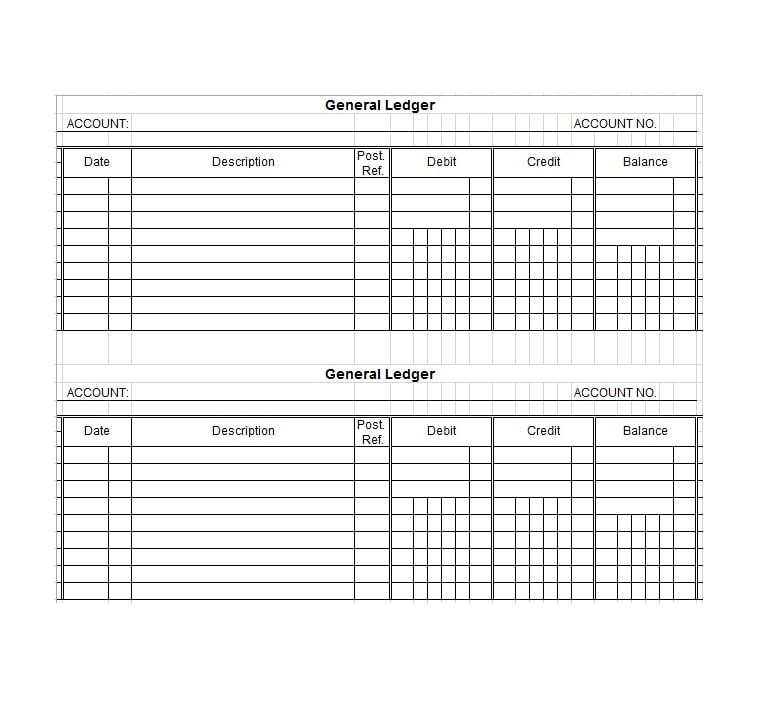

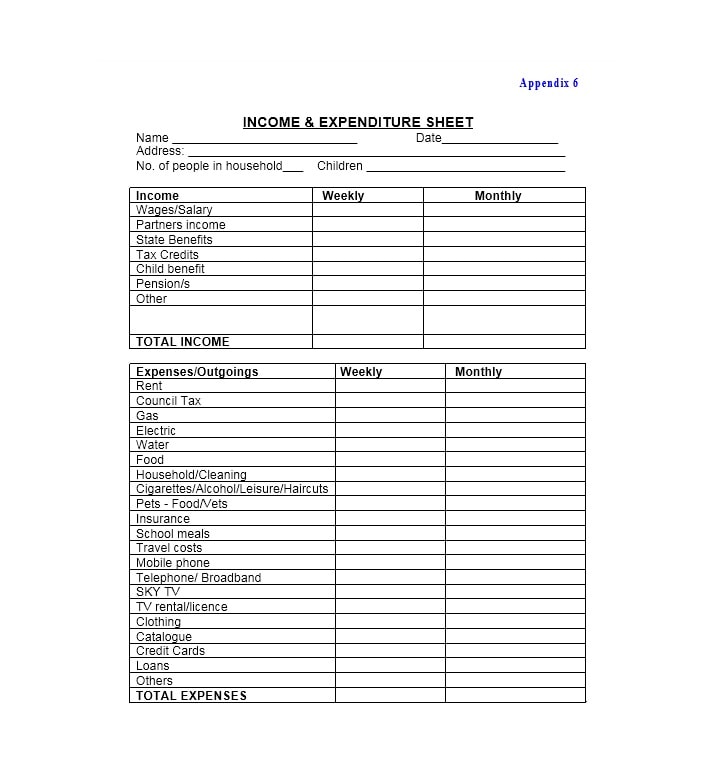
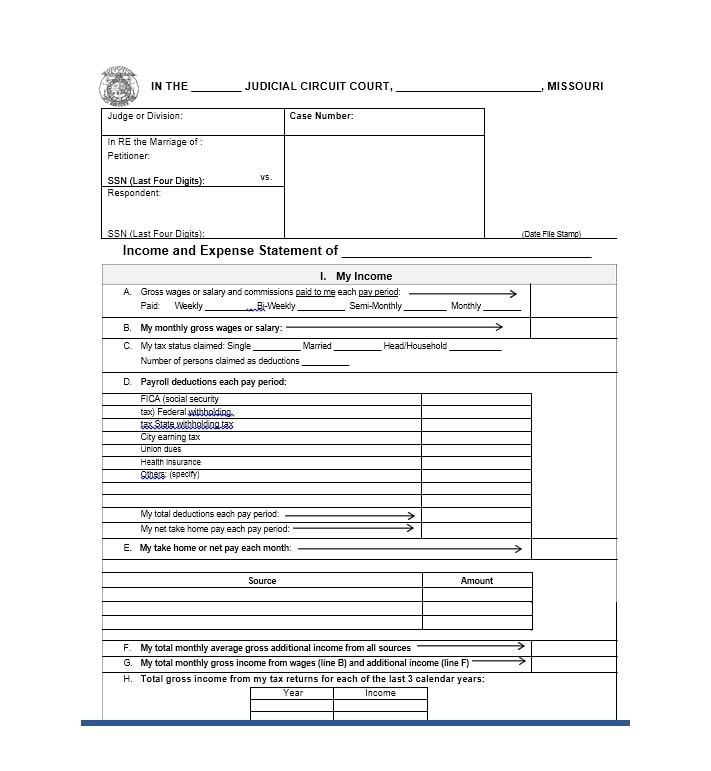



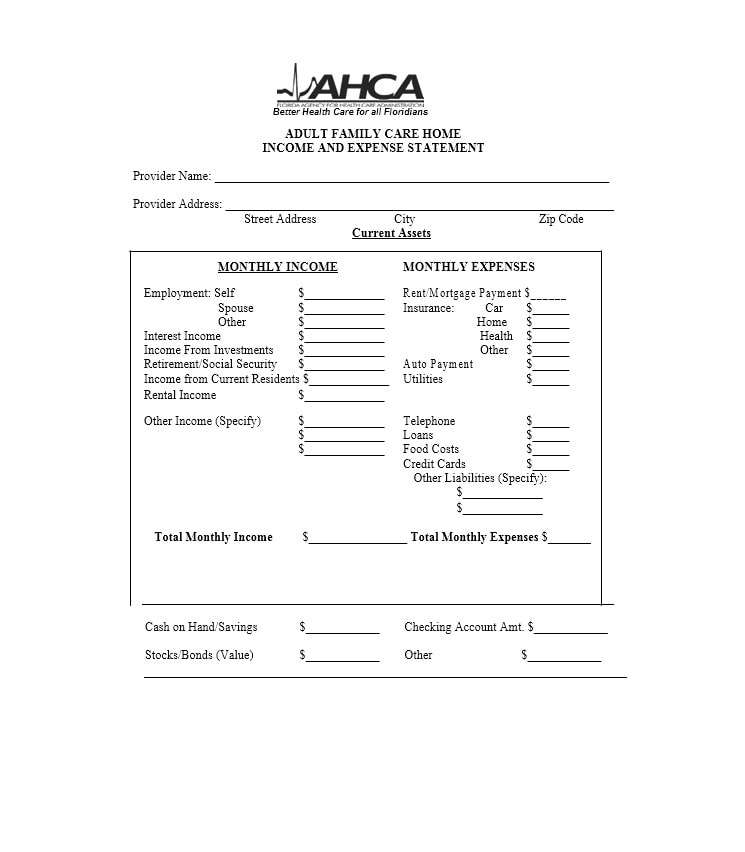
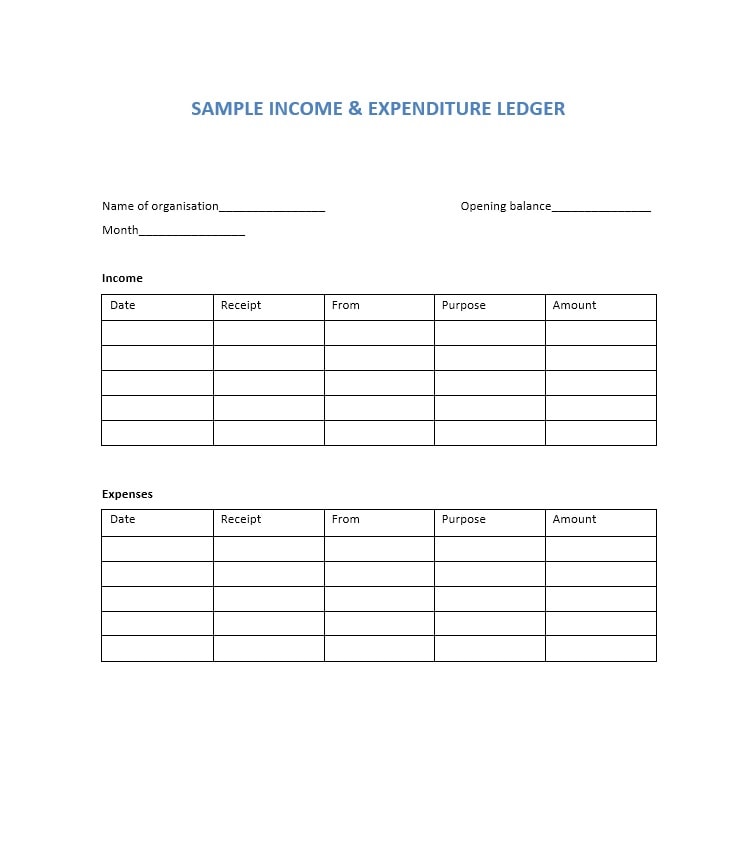


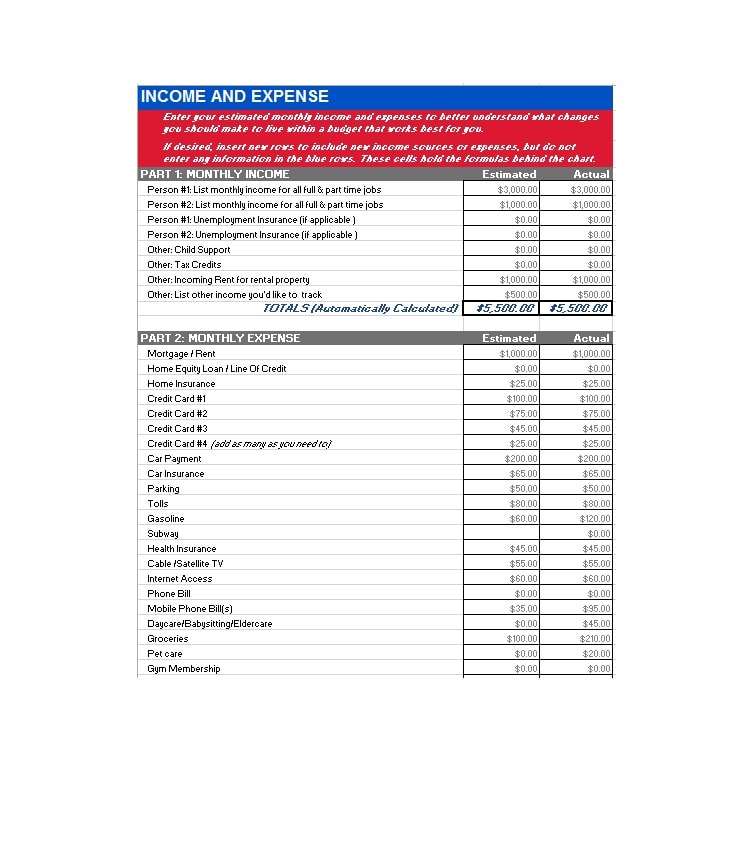

Tips for Successful Self-Employment Ledger Management
Here are some tips to help you effectively manage your self-employment ledger:
- Maintain Regular Updates: Consistently record your income and expenses to avoid falling behind and ensure accuracy.
- Separate Personal and Business Expenses: Keep personal and business transactions separate to simplify your record-keeping and tax reporting.
- Save Receipts and Invoices: Keep copies of receipts, invoices, and other supporting documents for each transaction. This helps in case of audits or disputes.
- Review Your Ledger Frequently: Regularly review your ledger to identify any errors, discrepancies, or missed entries.
- Seek Professional Advice: If you are unsure about certain transactions or tax implications, consult a tax professional or accountant for guidance.
- Use Accounting Software: Consider using accounting software specifically designed for self-employed individuals. These tools can automate many aspects of record-keeping and tax preparation.
Conclusion
A self-employment ledger is a valuable tool for managing your finances and optimizing your tax refund as a self-employed individual. By maintaining accurate records of your income and expenses, you can ensure tax compliance, identify deductions, and make informed financial decisions.
Follow the steps outlined in this article to create your self-employment ledger and use the provided examples and tips for successful ledger management.
Self-Employment Ledger Template – Download